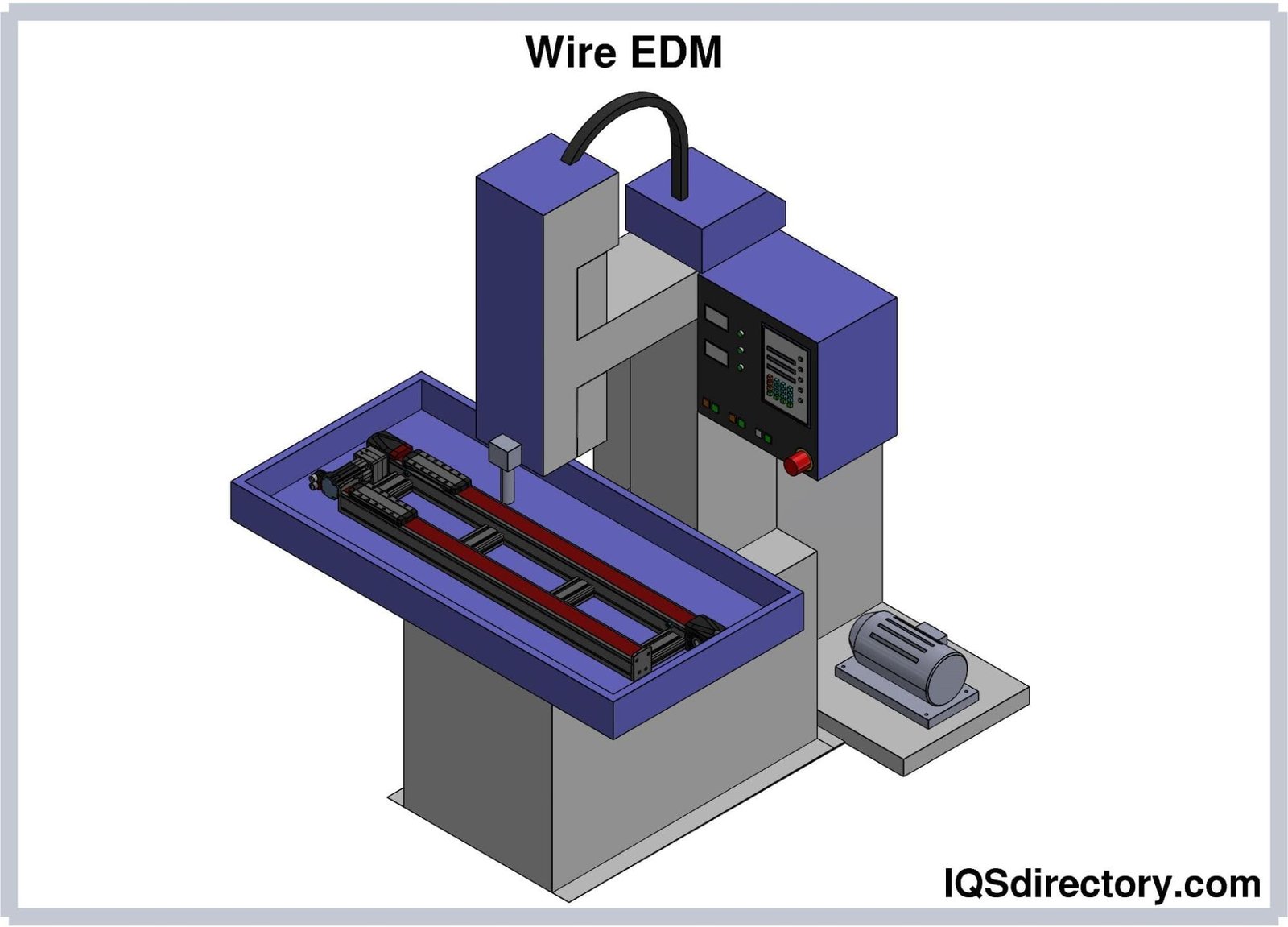
what is a CNC Wirecutting and how it works?
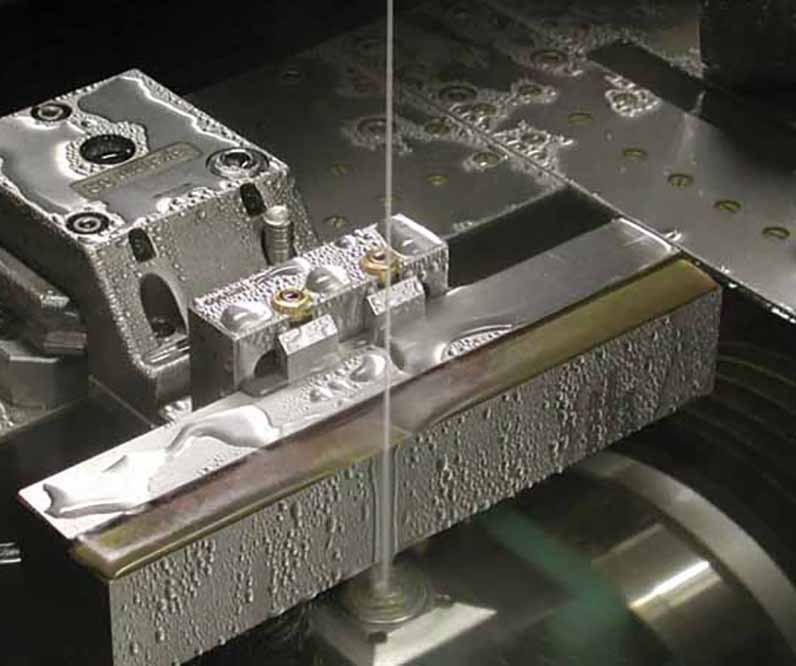
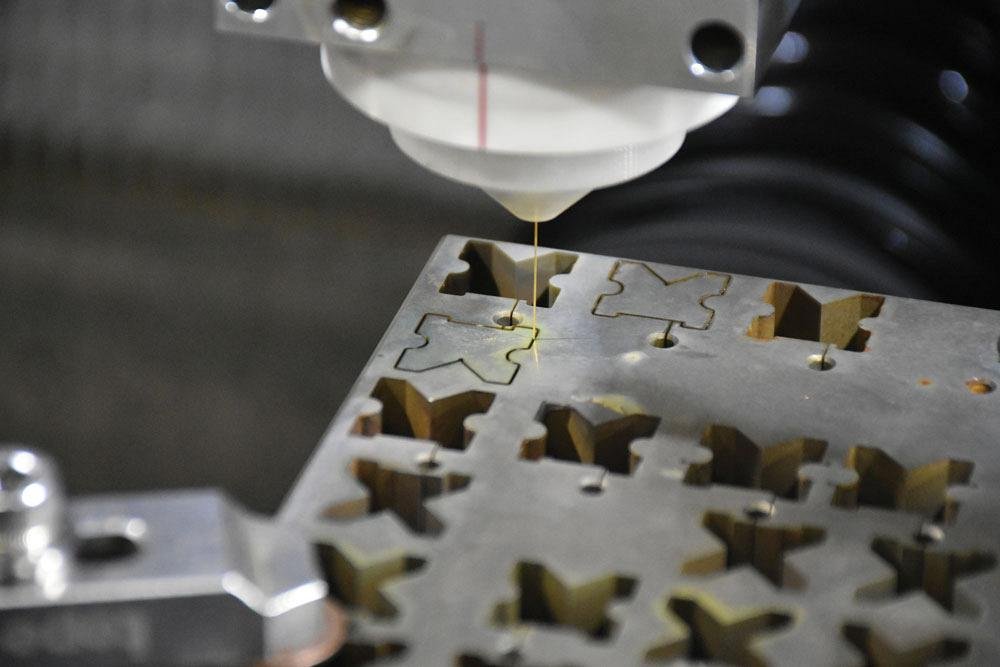
Wirecutting, also known as wire electrical discharge machining (WEDM), is one of the most powerful and advanced technologies in the metal cutting industry. It involves using a conductive wire and a combination of electric current and electric spark to precisely cut complex metal parts, as well as very small and detailed components like cracks and crevices. Due to its precision and unmatched cutting power, wire-cutting is widely used in various industries including automotive, aviation, machinery, electronics, and many others. The process involves passing an electric current through the wire, creating heat between the workpiece and the wire, leading to electrical discharge and cutting of the piece. This essentially causes an instantaneous melting of the part, enabling the cutting process.
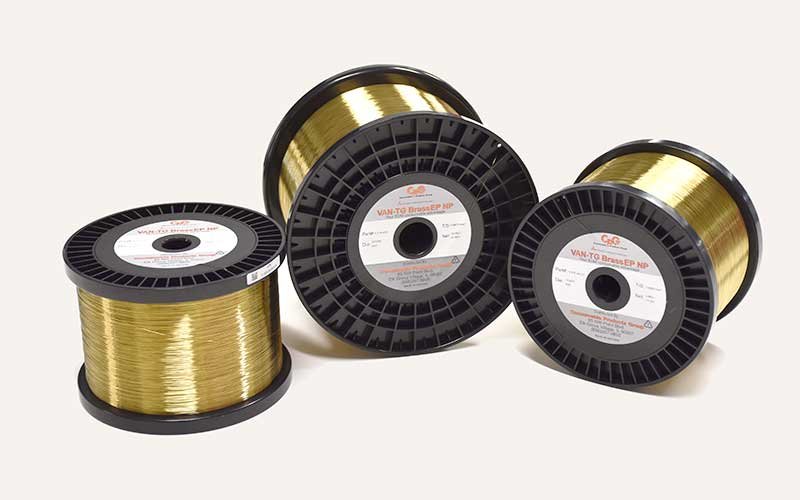
The wire used in wirecutting is extremely thin (about 25 microns) and operates within a dielectric liquid (distilled water), where the instantaneous melting occurs. In wirecutting, there is no physical contact between the wire and the workpiece; a gap is maintained between them, filled by the dielectric liquid. This liquid prevents debris from being ejected from the workpiece and also helps control the temperature of the arc. Therefore, wire cutting can be performed on conductive metals, and if the conductivity of the piece is low, the electrical discharge may not occur effectively. Next, we’ll discuss the steps involved in the process and the advantages of using wirecutting.
“Wirecut” is a term derived from the combination of two words: “wire” and “cut”. “Wire” refers to the conductive wire, and “cut” refers to the act of cutting. Thus, “wirecut” literally means cutting using a conductive wire. This term specifically refers to a method of cutting metals using a conductive wire and electric current, which is utilized in a wirecut machine.
The wirecut machine (also known as Wire EDM, standing for Wire Electrical Discharge Machining) employs electrical discharge machining (EDM) technology. In this process, an electric spark is used to remove material from the workpiece, a technique widely used in industrial part manufacturing. The conductive wire in the wirecut process is continuously and precisely moved, and through electrical sparks at specific points, cuts are made in the material. Typically, the conductive wire in wirecut machines is made of tungsten or nickel-titanium, known for their high mechanical properties and resistance to heat and pressure. The size of the conductive wire varies depending on the application and cutting needs, available in different sizes and diameters.
The wirecut machine features a mechanism that moves the conductive wire with high speed and precision. As the wire moves and creates electrical sparks at specific points, it comes into contact with the material, cutting it with high efficiency. Additionally, during the cutting operation, the wire is continuously fed, allowing for the creation of parts with complex and precise shapes.
Latest Articles in your inbox
Subscribe to our newsletter to get the newest manufacturing and industrial services articles in your inbox once a week.