Types of Lathes (Turning Machines) and Their Applications
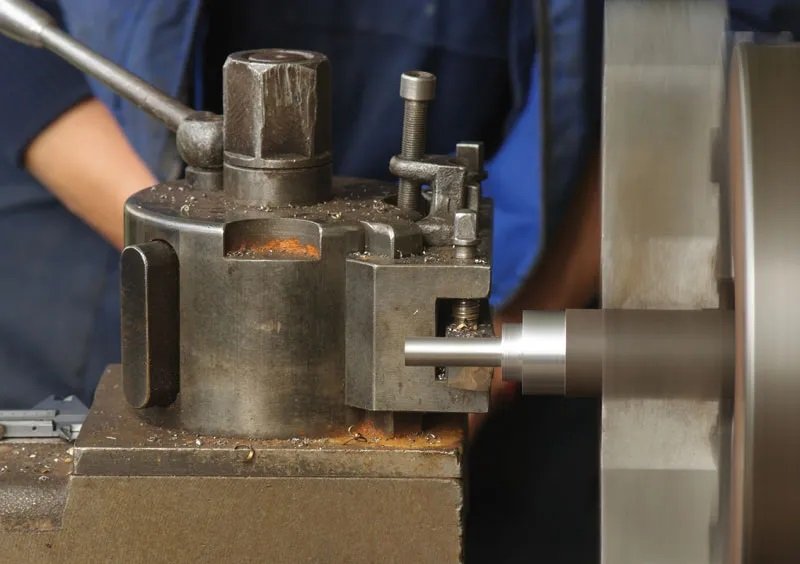
Tool-Making Lathe
The difference between these lathes and others is that tool-making lathes have greater precision. Some of them are equipped with special devices for more precise turning tasks. Their main purpose is to create tools and templates for production factories and lathes. They are used for both small and large works and are usually available in both benchtop and stand-mounted forms. The benchtop version is used for turning small and short parts with a small diameter, while the stand-mounted version is a relatively large and precise lathe with various speeds and an accurate braking system.
- Usage: Primarily used for producing tools and templates in production lathes and factories.
- Feature: Offers high precision in tool preparation.
- Varieties: Includes benchtop models for small, short-diameter parts, and stand-mounted versions with a braking system for greater accuracy in larger diameters and lengths.
Large Diameter and Length Lathe
- Application: Suited for processing workpieces with substantial length and diameter.
- Characteristics: Known for robust strength and superior cutting capabilities.
Small Benchtop Lathe
This type of lathe is used for training and small turning works. Since most of the work is done between two tailstocks, it is referred to as a tailstock lathe. Additionally, because it is used for training and small jobs, the motion transmission is usually belt-driven. In terms of size, they are divided into two forms: small benchtop lathes and small stand-mounted lathes.
- Purpose: Ideal for educational settings and small-scale lathe operations.
- Specialty: Efficient in turning parts between two centers.
- Types: Range from small benchtop lathes to slightly larger models with stands.
Face Lathe Machine
Works that have a large diameter and relatively short length are turned using this machine. Other uses include making locomotive wheels in locomotive factories and making flywheels (balance wheels).
- Use: Employed for tasks involving large-diameter yet short-length items, such as manufacturing locomotive and airplane wheels.
Heavy-Duty Normal Lathe
These lathes are used for turning works that have a large diameter and length. The size of their table and the height of the main axis of the machine to the rail are relatively large. For some of these lathes, a piece is placed near the main axis on the rail. This piece can be removed to turn larger diameter parts and is also used for special turning tasks. Generally, these machines are not designed for very high speeds, but they have a lot of cutting power and can remove a large volume of chips in a set time.
- Application: Suitable for drilling and heavy-duty tasks.
- Key Feature: Equipped with three systems for enhanced versatility. It’s designed for stability with a rotational movement and operates at lower speeds for precision work.
Vertical Lathe
As the name suggests, this lathe is positioned vertically. The tool holder is in the form of a multi-sided prism that can move vertically in a linear motion. The chuck of the machine is very large, positioned vertically, and rotates, suitable for holding heavy workpieces. It is also used for drilling and is generally not very fast due to its relatively heavy weight.
Normal Softened Lathes
These lathes are often used in production because they have a high production power and are built heavier. They have more speed stages, making them very suitable for large tasks. They are also superior in strength and durability compared to other machines and can be used for limited production.
Latest Articles in your inbox
Subscribe to our newsletter to get the newest manufacturing and industrial services articles in your inbox once a week.