Types of plasma cutting processes
The performance of different plasma cutting systems is not done in the same way and several processes have been designed to improve cutting quality, arc stability, reduce noise and increase cutting speed under different mechanisms.
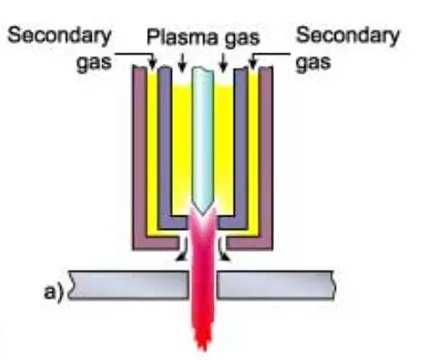
1- Dual Gas Cutting
The dual gas plasma cutting process essentially operates like the conventional plasma cutting system but with a key difference: a secondary shielding gas is introduced around the nozzle. The presence of this secondary gas enhances the constriction of the arc and helps in removing molten materials from the cut surface.
The advantages of this method compared to conventional plasma cutting include:
- Reduced Risk of Fire: The use of dual gases minimizes the risk of double arcing, which can cause fires.
- Higher Cutting Speed: The combination of gases can lead to faster cutting speeds.
- Reduced Edge Rounding: The top edge rounding on the cut surface is lessened, leading to cleaner and more precise cuts.
The gas forming the plasma is typically argon, argon-hydrogen, or nitrogen. The choice of the secondary gas depends on the metal being cut. This gas selection is crucial as it affects the quality of the cut, the speed of cutting, and the overall efficiency of the process. By optimizing the gas combinations, dual gas plasma cutting can offer improved performance for a variety of metal types and thicknesses.
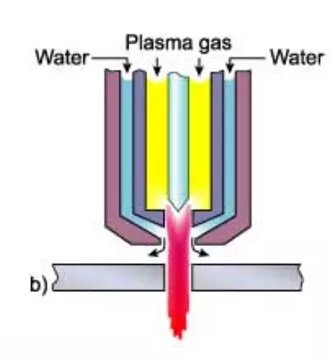
2- Water Injection:
In this process, nitrogen is typically used as the plasma gas. Water is injected radially (vortex injection) to increase the constriction of the plasma arc. The temperature also significantly increases up to 30,000 degrees Celsius.
The advantages of this method compared to conventional plasma cutting include:
- improved cut quality and elimination of waste below the cutting surface.
- Increased cutting speed.
- Reduced risk of arc doubling.
- Decreased nozzle corrosion.
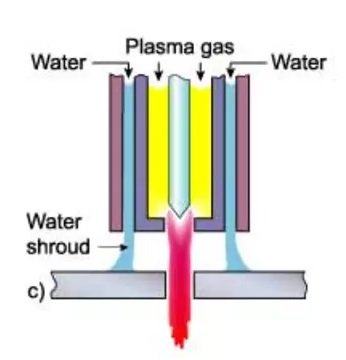
3- Underwater Plasma (Water Shroud):
Plasma cutting can also be performed in an environment covered with water. It is also suitable for cutting workpieces submerged up to 75 millimeters under the water surface.
Advantages of the presence of water compared to conventional plasma:
- Reduced smoke.
- Reduced noise.
- Increased nozzle life.
- Underwater plasma cutting.
For instance, the noise level from conventional plasma cutting is about 115 dB, cutting in an environment with a water shroud is about 96 dB, while noise from cutting underwater is reduced to 52 to 85 dB. Since this method cannot significantly increase the constriction of the formed arc, it cannot significantly improve the cut edge and cutting speed.
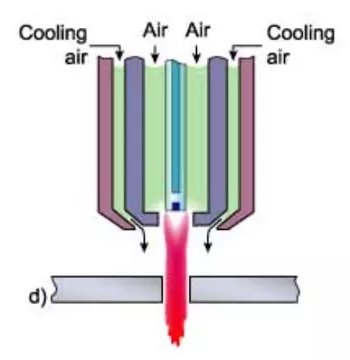
4- Air Plasma:
The plasma-forming gas, which is inert or non-reactive (such as argon or nitrogen), can be replaced with air. However, in this case, it is necessary to use a special electrode made of hafnium or zirconium installed in a copper holder. Air can also replace water for cooling the torch. The advantage of an air plasma torch is that it uses air instead of expensive gases. It should be noted that although the electrode and nozzle are replaced after their useful life has ended, hafnium electrodes are more expensive compared to tungsten electrodes.
5- High Tolerance Plasma Cutting:
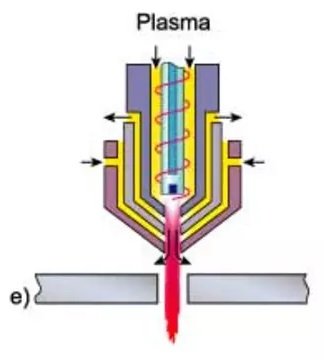
To improve cut quality and compete with high-quality laser cutting systems, high-tolerance plasma arc cutting (HTPAC) systems have been developed. This method operates by rotating the generated plasma during injection into the nozzle aperture, and a secondary gas flow is injected at the bottom of the nozzle to maintain rotation. In some systems, there is a separate magnetic field around the arc.
Advantages of HTPAC systems include:
- Narrower cut groove.
- Better cut quality compared to conventional plasma cutting, approaching laser cutting quality.
- Minimal distortion due to the small heat-affected zone.
HTPAC is a mechanized method that requires precise equipment and high speed. The main disadvantages of this method are that its maximum cutting thickness is limited to 6mm, and its cutting speed is slower than conventional plasma cutting processes, about 60 to 80% slower than laser cutting speeds.
Latest Articles in your inbox
Subscribe to our newsletter to get the newest manufacturing and industrial services articles in your inbox once a week.