what is Honing?
Do you know what honing is and what its industrial applications are?
One of the most important factors affecting the quality of industrial parts during operation is the smoothness of their surface when in contact with other parts.
Honing, along with other methods such as turning, grinding, and lapping, is one of the ways to achieve this smooth surface. However, the choice of each of these methods should be based on the technical aspects of the piece.
What we aim to examine in this article is the process of surface finishing in industries using the honing operation.
What is Honing?
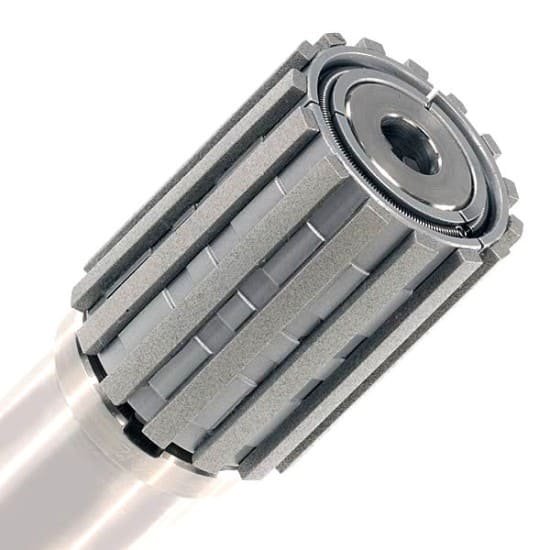
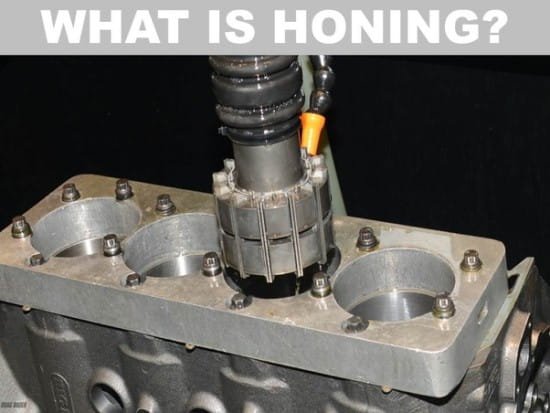
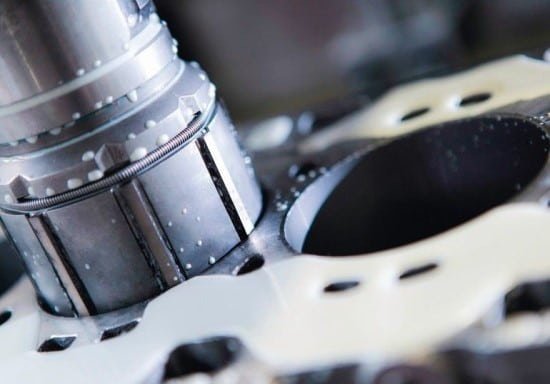
Honing is a final machining process, essentially the last step in removing material from cylindrical surfaces. The dimensional accuracy of this method is up to one micron, making it a time-consuming and costly process. During honing, an abrasive stone is used for surface material removal and finishing. This operation, combining reciprocating and rotational movements, results in a uniformly polished surface. For lubrication and cooling during the honing of non-ferrous metal parts, oil-in-water emulsions are used, while mineral oils are employed for iron alloys. It’s worth noting that the abrasive stone used in honing is applicable on many metal and non-metal surfaces. This stone can be sharpened, and its worn grains are replaced with sharp ones. Common abrasives in honing stones include aluminum oxide and silicon carbide, suitable for iron metals and non-iron metals like cast iron, respectively. Additionally, diamond stones are used in honing materials like ceramics. In summary, honing is a process aimed at improving the quality of surface finishes and eliminating surface waves from machined industries. The most important aspect of the honing process is precision and expertise, as any inaccuracy or lack of operator skill can lead to inefficiency and production delays.
Applications of honing
As mentioned, honing is a corrective process used to improve the quality of components in industries such as aerospace, automotive, oil and gas, and valve manufacturing. In this section, we will explain what the corrective operation of honing is and its role in the performance of components in these industries.
- One of the most important capabilities of honing for final part correction is the removal of lines that are residual marks from earlier material removal stages, like turning.
- Honing also creates fine crosshatch patterns to enhance the lubrication process.
- Finishing surfaces to eliminate waviness from the machining process and finalizing the diameter of a part are other critical applications of the honing operation.
Types of Honing Machines
Honing machines are produced in two primary forms: vertical and horizontal.
- Vertical Honing Machines: These are mainly used for operations on heavy parts. The vertical orientation of these machines makes them particularly suitable for handling large, heavy components that might be challenging to work with on horizontal machines.
- Horizontal Honing Machines: These are used for honing parts with high length-to-diameter ratios. Their horizontal layout is advantageous for elongated parts, providing ease of handling and precision in the honing process.
Regardless of their complexity, all honing machines are used in various industries, each having its specific applications. However, honing can generally be categorized into two types based on its application:
- Internal Honing: This is primarily used for finishing internal surfaces, such as the cylinders in automotive engines. Internal honing is critical for ensuring the smooth operation of moving parts within these cylinders.
- External Honing: This type is used for finishing external surfaces. External honing is important for components where the outer surface’s smoothness and uniformity are crucial for their functionality or assembly in larger systems.
Both types of honing are essential in various industrial applications, enhancing the performance and lifespan of machined parts.
Advantages of Honing
- High-Speed Process: Honing enables rapid correction of the shape of parts. This speed is particularly advantageous in high-volume production environments, where time efficiency is crucial.
- High Precision: Honing provides a high degree of accuracy in improving the geometric positioning and dimensions of parts. This precision is essential for applications requiring tight tolerances and exact dimensions.
- Excellent Finish: Honing produces exceptionally smooth and uniform surfaces. This quality of finish is particularly important for components that must move against each other with minimal friction or for aesthetic purposes in visible parts.
- Cool Material Removal Process: Honing removes material without significantly increasing the temperature of the workpiece. This is important for maintaining the integrity of the material’s properties and for preventing heat-induced deformations or damages.
Latest Articles in your inbox
Subscribe to our newsletter to get the newest manufacturing and industrial services articles in your inbox once a week.